A DAO is a complex process but full of potential, especially considering the rapid development of the blockchain sector. Currently, leading DAOs hold a total of $28.3 billion in treasury stakes, with most of these assets in liquid form. However, building and operating a successful DAO involves many factors that need to be carefully considered, from choosing the right blockchain platform to avoiding errors in smart contracts. In this article, Financial Insight Daily will share how to create a DAO, the essential components every DAO should have, and the pitfalls to avoid to ensure long-term success.
Understanding the Importance of DAO
DAO is a governance entity that operates without any centralized authority. You can think of it as a business that doesn’t have a single owner. In fact, every member of the organization is considered an owner of the DAO, and the community of members manages its own governance.
A DAO is governed by computer code and should be managed using automated processes powered by programmable smart contracts. These smart contracts help facilitate transactions and governance processes without human intervention. The fundamental concept behind creating a DAO revolves around building digital organizations that can use digital assets and blockchain technology to facilitate operations.
Decentralized organizations can offer the following benefits to users:
- Adaptability to multiple industries and use cases.
- Greater transparency within operations.
- Extended resources for innovation and financial profit.
- Establishment of a foundation of trust among members.
- Better processing speed compared to traditional organizations.
In a DAO, the entire community governs the organization, and everyone involved in the community has voting power on decisions related to the DAO. Depending on the governance model, DAOs follow various voting systems and representation forms. For example, some DAOs use the principle of “one token, one vote,” while others may employ a system of delegation where individuals can assign proposal rights to other members.

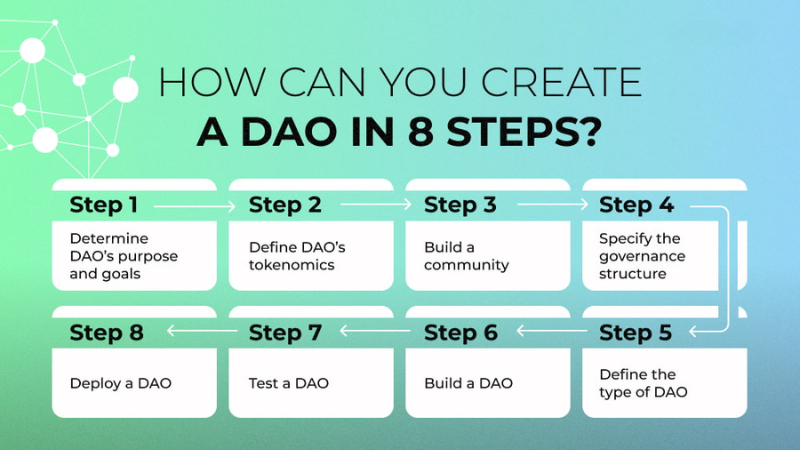
How to Create a DAO in 8 Steps
Creating a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) can be a highly rewarding venture, but it requires careful planning and execution. To ensure that you build a strong DAO without overlooking any critical aspects, we recommend following these eight steps:
Step 1: Define the Purpose and Goals of the DAO
Start by providing a clear and concise vision for your DAO. Develop a whitepaper that potential investors and partners can review to understand the project’s goals and recognize the benefits it offers to both them and your users.
Step 2: Define the Tokenomics Strategy for the DAO
A strong tokenomics model is crucial for attracting users and investors to your DAO. Clearly outline how your DAO will generate revenue, and explain the terms and conditions for engaging in financial activities such as token distribution, liquidity pool contributions, staking, lending, and more. You should also identify which tokens and coins, apart from the DAO’s native token, will be supported.
Step 3: Build the Community
A newly launched DAO needs dedicated users who will help it grow and guide its future development. To build a community, establish a presence on social media platforms like Twitter and Discord, run marketing campaigns, and offer exclusive benefits to early members.
Step 4: Define the Governance Structure
Set clear rules on how users will participate in the governance process of the DAO. The most common method is token-weighted voting, where one token represents one vote. The more tokens a user owns, the greater their voting power.
Step 5: Determine the Type of DAO
Decide on the type of DAO that aligns with your objectives. Common types include:
- Protocol DAO: Token holders manage the protocol and vote on proposed changes.
- Collector DAO: Unites NFT enthusiasts and creators to prove ownership of digital assets.
- Investment DAO: A transparent, globally accessible space for fundraising for DeFi projects and startups.
- Grant DAO: Enables users to pool funds in a grant pool and vote on fund allocation.
- Entertainment DAO: Helps creators build stronger communities around their collections and fund projects like play-to-earn games or metaverse activities.
- Social DAO: Strengthens social networks within the cryptocurrency community, offering space for communication, idea sharing, and fundraising. Membership often requires owning a certain number of tokens or an invitation.
Step 6: Build the DAO
Collaborate with a team of skilled blockchain consultants and developers capable of providing top-tier decentralized solutions. They will help you select the appropriate blockchain to serve as the foundation for your DAO and advise on necessary network support. You will also need to create robust smart contracts that are fault-tolerant and fast.
Step 7: Test the DAO
Before launching, perform thorough testing to ensure everything operates as expected and that no hidden bugs threaten the user experience or the platform’s security. QA engineers play a crucial role in fine-tuning system performance and ensuring its integrity.
Step 8: Deploy the DAO
Once everything is working smoothly, deploy your DAO to the mainnet. However, continue to gather user feedback to understand their concerns and preferences so you can make necessary improvements. Regularly conduct quality assurance tests to ensure the platform remains operational and secure.
By following these eight steps, you can create a robust and successful DAO that is designed to thrive in the rapidly evolving world of decentralized governance.
Risks Associated with Creating a DAO
When deciding to create your own DAO, it is essential to carefully consider several risks and limitations that may arise during the implementation and operation of the DAO. Here are the main risks you need to be aware of:
- Imbalance in Governance Power: The governance system of a DAO usually prioritizes decisions made by those who hold more tokens, as voting power is distributed according to the number of tokens owned. This reinforces loyalty, as large token holders are highly invested in the success of the DAO. However, it can also create an imbalance, with a small group of token holders able to dominate important decisions. This leads to incomplete decentralization and may cause the DAO to become more centralized, with decisions being made by a powerful minority group.
- Front-running: Front-running occurs when an individual buys or sells assets based on insider information before it is made publicly available on the market. In a DAO, members may have prior knowledge of investments or changes in asset values. This can lead to some users taking advantage of this knowledge to profit, such as by purchasing assets before the price rises.
If front-running is discovered, it can damage the reputation of the DAO and potentially cause significant financial losses for the platform if front-runners artificially inflate asset prices before the DAO has a chance to make its transactions. - Operational Costs: DAOs require cryptocurrency transactions, which come with gas fees for validating transactions and storing them on the blockchain. Gas fees vary depending on the network and fluctuate throughout the day based on supply and demand. For example, at the time of writing, the average transaction fee on Ethereum is $3.84, but this number can double when the network is congested.
Creating a DAO can be a great opportunity to build a decentralized and self-governing organization, but it requires thorough preparation and a smart strategy. When pursuing this idea, you need to ensure that your DAO has a clear vision, a strong community, and an effective governance model to help the organization operate sustainably in the long run. By following the correct steps to design and implement a DAO, from building tokenomics to deploying smart contracts, you can minimize risks and maximize the chances of success.
