Central bank interest rates impact on monetary policy is a big deal for your wallet and the whole economy. Think of these rates as the ship’s wheel that helps steer where things go. Banks tweak these numbers and like magic, your loans and the money in your pocket feel the change. We’ll crack open how these rate games work and how they toss ripples through prices and jobs. Ready to see why your savings and shopping trips depend on these interest decisions? This is the compass you need to navigate the twisty waters of economic change. Buckle up and dive into the world of rates, from your own budget to the nation’s cash flow.
Understanding Central Bank Rate Decisions and Their Economic Impact
The Mechanics of Interest Rate Policy and Monetary Adjustments
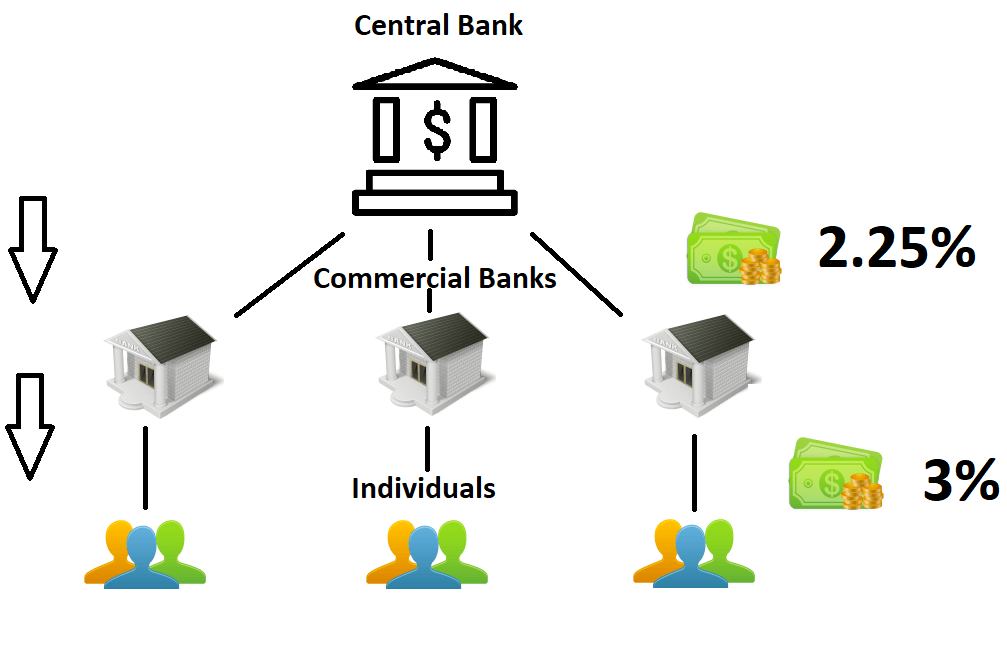
Central banks have a big job: they steer our economy. They decide how much it costs to borrow money. This is called the interest rate policy. Think of it as the price tag on money. Just like any price, it affects how much we want to buy or borrow. When central banks change this price, it’s a big deal. Interest rate policy affects everything from how much you pay for a loan to how much businesses invest in new ideas.
Let’s look at the federal funds rate. This is a rate that banks charge each other for loans. It acts like a guide. When this rate goes up, your bank loan may cost more. When it drops, loans can be cheaper. Big decisions on this rate can either help our economy grow or slow it down.
The Ripple Effect of Central Bank Decisions on Inflation and Growth
A central bank rate decision is like throwing a stone into a pond. It makes ripples. These ripples spread out and can make things shake up. One big ripple is inflation or how much things cost over time. If prices rise too fast, it’s hard for families to keep up. So central banks use their rate tools to target inflation. They aim to keep it low and stable.
Another ripple hits growth. This is all about how our economy expands. If a bank rate goes up, it gets harder to borrow. People might buy fewer things, and businesses might slow their roll. But if rates go lower, it’s like opening the floodgates. Money flows easier, and everyone wants a piece of the action. This is when you see people spending more, and businesses grow faster.
Central banks have to be careful. They don’t want those ripples to turn into waves that can flip the economy’s boat. It’s like being a captain at sea. They must know when to steady the ship or when to sail full speed ahead. That’s why these rate decisions are super important. They touch everything from your pocket to the nation’s wallet!
The Role of Interest Rates in Economic Stimulation and Credit Dynamics
How Lower Lending Rates Can Spur Economic Activity
Let’s talk about one big wheel that turns the economy: interest rates. Picture yourself with money to lend. If you charge less interest, more pals might borrow from you, right? That’s what central banks do. They lower costs to borrow, hoping businesses and people go, “Wow, cheap loans! Let’s spend!” This can mean new jobs, more things built, and folks buying more stuff. When cash flows, the economy grows.
The Balance between Credit Expansion and Macroeconomic Stability
But it’s like walking a dog on a leash – too much freedom, and things can go wild. If loans are too easy to get, people might borrow more than they can pay back. Then, trouble hits. Prices for everything go up, what we call inflation. And too much inflation isn’t cool. It makes our money buy less stuff. That’s why central banks tweak rates. It’s to keep the economy just right – humming along without running off or slowing down.
Big brains at the central bank watch it all. They change rates to hit that sweet spot: not too hot, not too cold. When they hike rates, it’s like tapping the brakes. It means “Whoa, easy on the spending, friends.” Spending slows, and so does inflation. When they cut rates, it’s like hitting the gas pedal. “Let’s roll and grow!” they’re saying. But what’s the right call? It’s tricky. They must be wisecrackers about timing and how much to change.
And hey, we’re not just talking small change. If rates go up, folks with loans or mortgages say, “Aw, man, my payments are bigger!” But savers cheer, “Yes! More cash for me!” If rates fall, it flips. Borrowers are happy, savers not so much. It’s a tough balance to strike.
To make it all work, the central bank uses some tools. Quantitative easing? That’s where they buy stuff to pump money into the banks. Or they might sell stuff off (open market operations) to pull some cash out. They can even say, “Banks, hold onto more cash” (reserve requirement ratio), so there’s less to lend out. It’s all about guiding the money river – making sure it flows nicely, not too fast or slow.
Listening to the central bank’s vibes is key. They drop hints about what they’re going to do. Watch them close, and you might guess the next move. That helps everyone: businesses, families, and investors.
In the end, it’s all about keeping the economy running smooth, like a well-oiled bike. We want growth, but no crazy speed wobbles. It’s a big job, but somebody’s gotta do it. And these interest rate wizards, they’re up in their towers, watching everything with their calculators and crystal balls, making the calls to keep us cruising steady. The better they are, the better we roll. So, now you get how this interest rate thing is a huge deal for all of us.
Assessing the Impact of Interest Rate Changes on the Housing Market and Consumer Debt
The Consequences of Mortgage Rate Fluctuations for Homebuyers
When central bank rate decisions change, so does the housing market. Here’s how. Say the central bank hikes rates. This often causes mortgage rates to rise too. Higher mortgage rates mean homebuyers will pay more over time for the same house they could have bought cheaper earlier. For many, this might mean choosing a smaller home or waiting altogether.
Let’s talk numbers. If mortgage rates go up by 1%, that could increase a monthly payment by hundreds of dollars. Pricey, right? This can discourage folks from buying. When fewer people can buy homes, demand drops, and house prices might stall or even fall. A rate hike can lead to tougher times for sellers and buyers.
The Broader Implications of Borrowing Costs on National Debt Service
When central banks tweak the interest rates, the effects aren’t just on homebuyers. Let’s dive deeper. When governments borrow money, they too have to worry about interest rates. These rates affect how much it costs them to borrow. If rates go up, governments pay more just like homebuyers do. This can mean less cash for other important things like schools or roads.
The bottom line is, higher lending rates make debts pricier to manage. This can apply brakes on the economy and make folks think twice before using their credit cards or taking out loans. In the end, when governments and people cut back on spending, this often slows economic growth. But remember, this same tool, changing interest rates, can also speed up the economy when needed by making borrowing cheaper. It’s all about balance in the world of monetary policy.
Forward-Looking: Anticipating Central Bank Moves and Preparing for Future Trends
Strategies Central Banks Use to Signal Future Rate Adjustments
Central banks have big jobs. They keep the economy stable. They do this through rate decisions and policy moves. They decide the cost of borrowing money. Their choices can slow down or speed up the economy. They must be clear about what they’ll do next. This helps banks, investors, and businesses plan ahead.
One way central banks signal future moves is by talking. They give speeches and put out reports. They might say if they’re worried about high prices or if the economy needs a boost. This talk is a sneak peek into what they might do next.
Another clue is data. Central banks look at things like job numbers and how much stuff costs. When these numbers change, central banks might change rates too. They also hold meetings, and the minutes of these meetings can give hints. The notes might show if they think about raising or lowering rates. This is like a treasure map for predicting rate changes.
Understanding Economic Indicators to Forecast Interest Rate Trends
Now, let’s think about the future. To know what will happen, you have to understand clues called economic indicators. These are like signs that tell us if the economy is healthy. If you know these signs, you can guess what central banks will do next.
Economic indicators include many things. The consumer price index, or CPI, shows if things are getting more expensive. When CPI goes up, things cost more. Central banks may raise interest rates to stop prices from rising too fast.
Another sign is how much stuff a country makes and sells. If a country is doing well, making and selling a lot, central banks may increase rates. This can stop the economy from getting too hot.
Job reports are also important. If loads of people have jobs, it means folks have more money to spend. This can lead to higher prices. Central banks keep a close eye on jobs to decide on interest rates.
One more clue is the health of other countries’ economies. If other places do well or have troubles, it can affect us too. Central banks think about this when they set rates.
By checking these signs, we can make smart guesses about future rates. In simple words, when prices soar, rates might go up. When the economy slows down, rates might drop.
Knowing these clues helps everyone. It’s like weather forecasting. Just as you grab an umbrella when skies are gray, businesses and people change plans based on rate clues. They borrow money or save more depending on what they think will happen. Getting these guesses right means making or saving money. Getting them wrong can cost a lot.
Central banks have a tough job steering the economy just right. But by sending out signals and clues, they help everyone prepare. It’s like being on a ship. The central bank is the captain, and rate signals are the stars that guide us. If we read the stars well, we can all sail smoothly into the future.
We’ve seen how central bank rate decisions shake up the economy. From daily buys to home loans, these rates touch lives and markets. By shifting interest rates, central banks aim for balance: they want growth, but not too fast, to keep inflation in check. Our wallets feel it when these rates change, especially if we’re looking to buy homes or pay off debts.
Interest rates aren’t just numbers. They’re tools that can help nations prosper or, if handled poorly, spiral into instability. Central banks must tread carefully to hit that sweet spot. They even give hints on what’s next, so the smart move is to watch and plan.
Knowing how rates work and what the future might hold positions us to make better choices. We can protect our finances and maybe even find chances to grow our money. Let’s stay sharp and ready for what comes next in the economy’s beat.
Q&A :
How do central bank interest rates affect monetary policy?
Central bank interest rates, often referred to as the “policy rates,” are critical tools for monetary policy. Changes in the interest rates can either stimulate or cool down the economy. When a central bank lowers interest rates, it makes borrowing cheaper, which can boost spending and investment. Conversely, raising interest rates can help to slow inflation and temper an overheating economy by making borrowing more expensive, which typically reduces consumer spending and investment.
What happens when a central bank changes its interest rates?
When a central bank changes its interest rates, it directly influences the cost of credit for banks and subsequently for consumers and businesses. Lower interest rates tend to encourage borrowing and spending, which can lead to economic growth. Conversely, higher interest rates generally lead to decreased borrowing and spending, which can slow down inflation and economic growth. These changes can have ripple effects on currency value, stock prices, and government bond yields.
Why might a central bank raise interest rates?
A central bank might raise interest rates to combat inflation. When prices for goods and services rise too quickly, a central bank may increase interest rates to make borrowing more expensive, which can decrease consumer spending and business investment, thereby slowing down the economy and reducing inflationary pressure. Raising rates can also attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the country’s currency.
What is the impact of central bank interest rates on the forex market?
Central bank interest rates have a significant impact on the foreign exchange (forex) market, as they influence the relative value of currencies. When a central bank raises interest rates, it often leads to an appreciation of the national currency, as higher rates provide better returns to investors, making the currency more attractive. Conversely, cuts in interest rates can result in currency depreciation, making it less appealing to investors.
Can central bank interest rate decisions affect employment?
Yes, central bank interest rates can have an impact on employment. By influencing economic activity through rate adjustments, central banks can indirectly affect the job market. Lower interest rates are generally intended to boost economic growth, which can lead to more hiring and a reduction in unemployment. On the other hand, increasing interest rates can slow down economic expansion and possibly lead to higher unemployment if businesses reduce investments and hiring.