In today’s blockchain space, solutions for cross-chain communication (interoperability) are becoming increasingly important. One standout platform in this field is LayerZero. So, what is LayerZero and how does it benefit the blockchain ecosystem? This article provides an in-depth look at LayerZero.
What is LayerZero?
LayerZero is a multi-chain interoperability protocol that enables different blockchains to connect and exchange data directly and securely. While most traditional blockchains can only operate independently, this protocol solves this problem by creating an infrastructure that connects blockchains, forming an unlimited linked network.
This protocol is not just a bridge between blockchains but also an open protocol that does not require blockchains to modify their structure. This means LayerZero can be integrated into any blockchain, whether existing or newly created, without encountering obstacles from technical limitations.
With LayerZero, decentralized applications (dApps) and DeFi platforms can operate across multiple chains without worrying about blockchain compatibility, while improving transaction efficiency and reducing costs. This enhances the flexibility and potential of the blockchain ecosystem, enabling applications to run more efficiently and reach a wider audience.

How does LayerZero work?
LayerZero’s functionality is built around three main components: Endpoint, Oracle, and Relayer. Each component plays a critical role in ensuring the validity and reliability of cross-chain transactions. Let’s take a closer look at how this system works.
Structure of LayerZero
LayerZero is built on three basic components: Endpoint, Oracle, and Relayer. Each has a distinct role, helping to connect and ensure the accuracy of cross-chain transactions.
Endpoint
The Endpoint is the interface through which users interact with LayerZero. It can be seen as a “client” operating on various blockchains, responsible for sending and receiving messages between networks. The unique feature of the Endpoint is that it does not store data but uses ultra-light nodes to reduce transaction costs. This also allows users to build applications on the Endpoint without worrying about complex data storage.
The endpoint is divided into four main sections
- Communication: Facilitates the setup and transfer of information between networks.
- Validation: Ensures the authenticity of transactions and messages.
- Network: Manages network connections and maintains links between blockchains.
- Library: Contains core modules for each network. When a new network wants to integrate with LayerZero, they can simply add the module to the library, making integration easy.
Oracle
An Oracle is an independent third-party service that works separately from other LayerZero components. Its primary task is to read the block header from one chain and transfer it to another. Oracles ensure data accuracy and help this protocol validate the authenticity of cross-chain information transmission. Currently, this protocol uses Chainlink, a leading Oracle service in the market, for this function.
Relayer
A Relayer is also an off-chain service, similar to an Oracle, but instead of fetching block headers, it retrieves transaction proofs for specific transactions. Users can create their own Relayer services. Relayers store data off-chain, which reduces the load on blockchains and makes the transaction process faster and more efficient.

Detailed operation mechanism of LayerZero
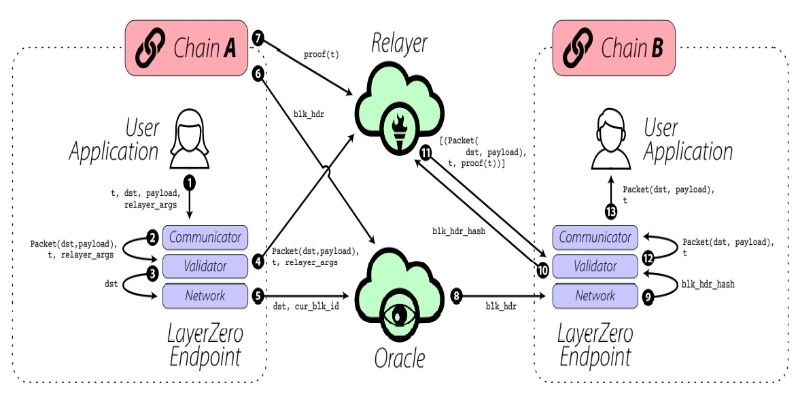
LayerZero executes cross-chain transactions through a 13-step process. This ensures that all transactions between blockchains are accurate, secure, and fast. Below is a detailed description of this operational mechanism.
Send transaction
When a user initiates a transaction, the application on chain A sends a transaction with a specific identifier to the LayerZero Communicator. This transaction includes:
- t: The unique transaction ID of T.
- dst: The identifier pointing to the smart contract on chain B.
- payload: Data to be transferred from chain A to chain B.
- relayer_args: Information describing the payment when using the Relayer service.
Package the transaction: The Communicator packages the transaction information (dst, payload) and sends it to the Validator along with the other details (t, relayer_args).
Confirm the transaction: The Validator sends the transaction ID (t) and destination chain info (dst) to the Network, notifying it to send the block header from chain A to chain B.
Request transaction proof: The Validator sends a packet containing the transaction details to the Relayer, asking it to fetch the transaction proof for transaction T from chain A.
Send block header to oracle: The Network sends the destination chain identifier and current block ID (cur_blk_id) to the Oracle, requesting it to fetch the block header from chain A and transfer it to chain B.
Read block header: The Oracle reads the block header from chain A, verifying its accuracy.
Fetch transaction proof: The Relayer reads the transaction proof from chain A and stores it off-chain.
Confirm block header: The Oracle confirms the block header on chain A and sends it to the Network on chain B after validating its correctness.
Send block hash: The Network sends the hash of the block header (blk_hdr_hash) to the Validator.
Transmit block header to relayer: The Validator forwards the block header hash to the Relayer.
Verify and send packets: Upon receiving the hash, the Relayer sends a list of valid packets and the transaction proof to the Validator.
Verify transaction: The Validator uses the transaction proof and block header to validate the transaction. If the data is valid, the Validator proceeds to process the transaction.
Complete transaction: Finally, the Communicator forwards the packet (dst, payload) and transaction ID (t) to the application on chain B, completing the cross-chain transaction.
Key features of LayerZero
LayerZero stands out with several unique features that enhance blockchain interoperability and support the development of decentralized applications (dApps) in the blockchain ecosystem. Here are some of the standout features of this protocol:
Superior interoperability: One of LayerZero’s greatest strengths is its ability to connect multiple different blockchains. This expands the potential of dApps, allowing them to operate across various blockchains without compatibility issues. DeFi platforms can also share liquidity and assets across chains, optimizing the user experience.
Flexible scalability: With its modular architecture, this protocol easily scales to support new blockchains. This ensures that developers do not have to worry about restructuring their blockchain to integrate LayerZero into their ecosystem. Additionally, this protocol supports multiple applications and transactions with low costs, minimizing the financial burden on users.
Security and transparency: LayerZero’s operational mechanism ensures high security for cross-chain transactions. By combining oracles and relayers, LayerZero guarantees that data is not altered or tampered with during transmission between blockchains. Transactions are encrypted and validated rigorously, protecting user information from potential threats.
Lower transaction costs: Compared to other cross-chain communication solutions, this protocol can significantly reduce transaction costs. There is no need for complex intermediaries or centralized systems, making LayerZero an optimal platform for fast and cost-effective transactions.

Practical applications of LayerZero
LayerZero is being widely adopted across various areas of the blockchain ecosystem, from decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain gaming to supply chain applications. Here are some practical use cases of this Layer:
Cross-chain DeFi: LayerZero enables DeFi platforms to connect with multiple blockchains, facilitating liquidity and asset sharing across chains. Users can execute cross-chain transactions without compatibility issues, creating diverse investment opportunities and optimizing returns.
Blockchain gaming: LayerZero supports the sharing of assets, data, and characters between different blockchain games, allowing players to move assets and participate in multiple games without worrying about chain compatibility.
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens): LayerZero enables the trading and transfer of NFTs across blockchains, opening new opportunities for the NFT market and making it easier for users to exchange digital assets across various platforms.
Supply chain: In supply chains, LayerZero can help connect data from various sources, improving transparency and efficiency in tracking products from production to consumer.
So, what is LayerZero? LayerZero is a powerful solution for addressing cross-chain communication challenges, paving the way for a more flexible and complete decentralized ecosystem. With its smart operational mechanism, high security and superior interoperability, this protocol is becoming a critical tool for the development of blockchain applications in the future. Anyone looking to enter the blockchain industry needs to understand LayerZero to fully leverage its potential.
Don’t forget to continue following Financial Insight Daily for daily updates on interesting and useful information.
